What is a definite article in English. How to use the article the
The article in English indicates the definiteness or indefiniteness of a noun, in other words, it allows us to understand what kind of subject / concept we are talking about: abstract or specific. The articles of the Russian-speaking person cause many difficulties, because in our language they simply do not. However, dealing with this unknown part of speech is not as difficult as it seems.
Article Functions
English has only two articles: a (an) and the - the first is used with indefinite nouns, and the second with certain. In order to better understand where and what to put, you need to consider each separately.
The Indefinite Article in English
Let's start with the indefinite article a (an). Its spelling changes depending on which letter (consonant or vowel) the noun begins with in front of which the article will stand.
Consonant letter: a dog - dog
Vowel: an apple - apple
The indefinite article has two features:
- only used when it comes to an abstract concept or object that is first seen;
- it is used with nouns only in the singular, since the article itself came from the numeral one.
The article a (an) indicates that the noun is not considered as a specific object, but as a lengthy concept. For example, a cup will mean a certain (any) item of utensils in the form of a cup, and not your favorite cup with the shape of a stormtrooper head from which you have been drinking coffee in the morning for the second year now. Thus, the indefinite article in English is used either when we encounter an object for the first time, and we still do not know anything about it, or when we talk about an abstract, collective concept.
The definite article in English
If you want to mention that very special morning cup in the conversation, you will need the definite article the. It came from the pronoun that (that) and is used in cases where it is known exactly what kind of object in question.
Free lesson on the topic:
Irregular English verbs: table, rules and examples
Discuss this topic with a personal teacher in a free online lesson at Skyeng School
Leave your contact details and we will contact you to register for the lesson.
Example: I met a man. The man was very strange - I met a man. The man was very strange.
In the first sentence, we first meet a stranger, in which case the word man is preceded by an indefinite article. In the second sentence, we draw a conclusion regarding the person we just talked about. It is no longer unknown, which allows you to put the definite article the before the word man.
The definite article the can be used with nouns in both singular and plural.
To finally understand a certain article, we can consider another example - the trilogy The Lord of the Rings (“Lord of the Rings”). Here, within the framework of one name, a certain article is used twice. This is due to the fact that in both cases we are talking about specific objects: about one single sovereign (Sauron) and about the only rings created by him. If the concept of “lord of the rings” meant a profession, then we could say a lord of rings, but that would be a completely different story.
The zero article, or when the article is not needed at all
The main difficulty in studying the articles of the English language is to remember in which cases they should not be used.
The noun does not always require additional refinement in the form of articles - sometimes other parts of speech take on their role. Articles are not used if:
- the noun has a pronoun (my, his, her, their, one’s, this, that, etc.);
- the noun has the words some, any, no;
- names of people or names of continents, islands, mountains;
- uncountable concept (advice, information).

Product table
As a rule, information is acquired faster if you consider it in a systematic table. We have prepared such a table for your convenience.
| The Indefinite Article a / an | The | Lack of article |
|---|---|---|
| This is one item from a variety of similar an apple - (some kind of) apple a cow - (some kind) cow |
It is known exactly what kind of object in question the apple - (the same) apple the cow - (the same) cow |
The noun has a pronoun (my, his, her, their, one’s, this, that, etc.) my apple - my apple this cow - this cow |
| The object is mentioned for the first time I met a man - I met (some) person |
This is the only object in the world the Earth - Earth |
The noun has the words some, any, no any piece - any piece |
| Profession designation a doctor - doctor an engineer - engineer |
There is an ordinal number or superlative in front of a noun the second floor - second floor the best singer - best singer |
Before the names of people or geographic features such as continents, islands, and mountain peaks Mary - Mary Eurasia - Eurasia Tasmania - Tasmania (island) Mount Everest - Mount Everest |
| Before the geographical names of countries formed by common nouns (as well as their abbreviations) The Russian Federation (The RF) - Russian Federation (RF) The United States of America (The USA) - United States (USA) The United Kingdom (The UK) - United Kingdom The United Arab Emirates (The UAE) - United Arab Emirates (UAE) |
Before the names of countries, peninsulas Kanada - Canada Spain - Spain Kamchatka - Kamchatka (peninsula) |
|
| Before the geographical names of countries in the plural The Netherlands - Netherlands The Philippines - Philippines |
If the word lake is before the name of the lake, the names of the bays Lake Baikal - Lake Baikal Bounty Bay - Bounty Bay |
|
| Before the names of oceans and seas The Volga - Volga (river) The Caribbean sea - Caribbean Sea The Atlantic Ocean - Atlantic Ocean |
It is an uncountable concept information - information knowledge - knowledge |
|
| Designation of cardinal points the east - East the qest - West |
Finding out when and how to use articles is easy enough. But in order to remember these rules and not to think each time before pronouncing or writing the next noun, you definitely need practice.
There are rules in any language, but there are exceptions. How to use articles in English? Saying with certainty in which place ‘a / an" is placed, and in which ‘the", may not be so simple. Fortunately, there are several rules that will help you with this, but for this you need to know which class of nouns you use.
The articles in the English language refer to official words serving as the main identifiers of nouns. The use of articles with names is directly dependent on whether they are specific or not. The use of articles in English is characteristic of most cases of the use of nouns in English. In this article, we will examine the use of articles in the English language.
Why do you need articles in English?
Do you know that the article is a part of speech that is not in Russian?
We change the accent and word order to give the phrase a shade, and in English the word order is strictly fixed.
See how the meaning of the phrase changes:
- I like the car.
- I like the car.
Feel the catch? In the first case, it is not clear what kind of car is involved, and in the second it is a specific machine.
In English, you can’t swap words, so the articles A, An and The are used to give the phrase the right shade.
Article Types
There are three articles in English:
the:
- Did you enjoy the party? - Did you like the party?
two indefinite articles in English:
- - the article a - is used if the following word begins with a consonant: I’m reading a book about England - I read a book about England
- - article an - if the word after it begins with a vowel: I read an interesting story - I read an interesting story
“Zero article” is the absence of articles: Does she like meat or fish? “Does she like meat or fish?”
Articles in English can appear immediately before a noun:
- She is an artist - she is an artist
In addition, articles in English can be separated from a noun using an adverb or an adjective:
- the newly renovated church - recently renovated church
- a beautiful young woman - beautiful young woman
The Indefinite Article A / An

The indefinite article a / an is the evolved Old English numeral “one”. This fact defines 2 basic rules for using this article.
because this is the former numeral, a / an can only be used with countable nouns (which we can count):
a car, a cup, a lamp, a bottle, an apple
- Have a drink. There is a bottle of wine in the fridge.
because this is the numeral "1", we can use a / an only with countable nouns in singular Plural The article disappears:
cars, _cups, _lamps, _bottles
- Have a drink. There are (several) _bottles of wine in the fridge.
the indefinite article distinguishes one object from a multitude of similar ones that are no different from it. You have a minimum of information about him.
- I had a sandwich for breakfast.
- There is a book on the table.
The definite article
The definitive article is nothing more than an abbreviated form of demonstrative pronouns this (this), that (that), these (these), those (those).
We will put the article before nouns, if it’s clear to us, it’s clear what kind of subject it is.
- The telephone is out of order. Let’s fix it. - Th ephone is not working. Let's fix it.
In this case, the phone is specific, this one that is in front of us and which we are going to fix.
The article matters this particular subject that we are talking about. We do not mean any kind of telephone, but a specific telephone, around which the whole situation unfolds.
- The computer has changed the world. - The computer has changed the world.
- The consumer decides which product to buy. - The consumer decides which product to buy.
The article can be used with both singular and plural nouns.
Lack of articles in English
Before plural nouns and uncountable nouns (uncountable nouns are those that cannot be counted: water - water, air - air, tea - tea, etc.). This item applies only to the indefinite article. It should be noted that with uncountable nouns, the pronoun “some” is often used instead of the indefinite article: Would you like some milk? - Do you want some milk? Some sources call the word “some” in this function the article.
Before breakfast, lunch, dinner, supper, if they do not have an adjective. Compare:
- We have breakfast at 9. - We have breakfast at 9 o’clock.
- We had a good breakfast. - We had a good breakfast.
Before the names of people, names of languages, names of games, as well as names of days of the week, months, public holidays.
- with mike
- in English
- on sunday
With the words bed, church, court, hospital, prison, school, college, university, sea, when these places are visited or used for their intended purpose. For example:
- To go to hospital - go to the hospital (as a patient, not on an excursion)
- To go to church - go to church (pray);
In the following established expressions, it is advisable to remember them:
- all day / night long, all day / night through, day after day, from morning till night, from dusk till dawn, day and night.
- at night, by day / night, at midnight, at sunset, for example, on time, in harmony, to take place, to catch cold
In expressions indicating the method of movement:
- by bus - by bus
- by plane, (by air) - by plane (by air)
- on foot - on foot

How to distinguish between definite and indefinite articles in English? ..
But the main difficulty for those who decide to learn English is the problem of choosing between definite and indefinite articles.
Let's look at examples and compare their use:
- Let’s buy the car. (Let's buy this car.) - Here we are talking about buying a certain car, which is already known to everyone.
- Let’s buy a car. (Let's buy a car.) - This example refers to any car, not a specific one.
In other words, the definite article in the English language is applicable to the special representative of any group of persons or objects. For example:
- He caught the rarest butterfly in the world. (He bought the rarest butterfly in the world.) - Obviously, there are many types of butterflies in the world, but we are talking about the rarest of them.
- She is going to catch a butterfly. (She is going to catch a butterfly.) - In this case, it’s not about a specific one, but about any butterfly. There are many butterflies, and she wants to catch any.
Article position in the sentence
The article in English is usually put before the noun and related words, if any:
- I see a shop. - I see a store.
- It is a big European furniture shop. - This is a large European furniture store.
But some such words may appear before the article:
The definite article the can be preceded by the definitions of all and both:
- All the books in my room are torn. “All the books in my room are torn.”
- Both the pens are not working. - Both pens do not work.
The indefinite article may be the words what, such and quite:
- What a loss! - What a loss!
- You were such a clown yesterday. “Yesterday you looked like such a clown.”
- It’s quite a long way. “It's a pretty long way.”
The indefinite article is placed after adjectives in combination with the adverbs too, as, so:
- It is too long a way to go on foot. “This is too much to walk.”
- He is as good a sportsman as any man of his age. “He is as good a sportsman as any other man of his age.”
That seems to be all that we need to know about the article in order to speak correctly.
Once again, in simple words and illustrative examples, we focus on the key points of using certain and indefinite articles.
Articles are an important part of the English language. But unfortunately, this topic is not always understood by Russian-speaking students. Because in their native speech, such a phenomenon is absent. rules for the use of articles must be studied by a person who wants to correctly use various means of the English language. And in some situations, small and seemingly insignificant articles even help to correctly understand the interlocutors.
What are articles and what are they
An article is one that is inextricably linked with a noun. It does not have its own meaning (translation into Russian), but conveys only the grammatical meaning.
In English, the article does not indicate the gender and case of nouns. It conveys in some cases the only one or but basically carries only the category of certainty-uncertainty. Based on this, there can be three situations with the article: its absence, indefinite and definite. Each of these three situations has its own specifics and its own rules.
The definite article was once formed from that. Therefore, in Russian one can often find the translation “this,” “these,” etc. Formally, this is not entirely true, because the service parts of speech have no translation, but in the case of the article, especially certain, this is often allowed. It is all about a special stylistic function that he can play in the sentence, pointing in a special way to objects and people.
The use of the article will be the topic of this article. We will consider various situations, give examples. There will be many cases of use, but do not be alarmed if you can not immediately understand everything and even more so remember. More and more immersed in the English language through constant studies, you will understand this logic and soon you can easily determine which article is needed in each case.
The definitive article before nouns
The classic case when it is necessary to use the article the in front of the name of the subject (person, animal) is the latter.
1. The named noun is one of a kind.
For example: the sun - the sun, the world - world.
2. The noun is unique in this situation.
Do you like the pie? - Did you like the cake?

3. This subject (man, animal) has already been mentioned in this conversation and therefore the interlocutors understand what (com) it is about.
I’ve got a cat. Her name is Lucy, she’s very cute. May I take the cat with me? - I have a cat. Her name is Lucy, she is very cute. May I take a cat with me?
4. Such article is also put in front of proper names when it is necessary to designate the whole family. For example: the Smiths.
The definite article before other parts of speech
Of course, the article the and any others are used only with nouns. Articles are not needed in front of other parts of speech. But it often happens that between the article and the related noun is a numeral or adjective. We will consider such cases.
1. A definite article is always put before ordinal numbers: the twentieth century - twentieth century.
2. The article the invariably is also placed before the adjectives: the brightest star is the brightest star.
3. It is necessary to use a certain article when designating a group of people united by a common attribute: the young - youth.
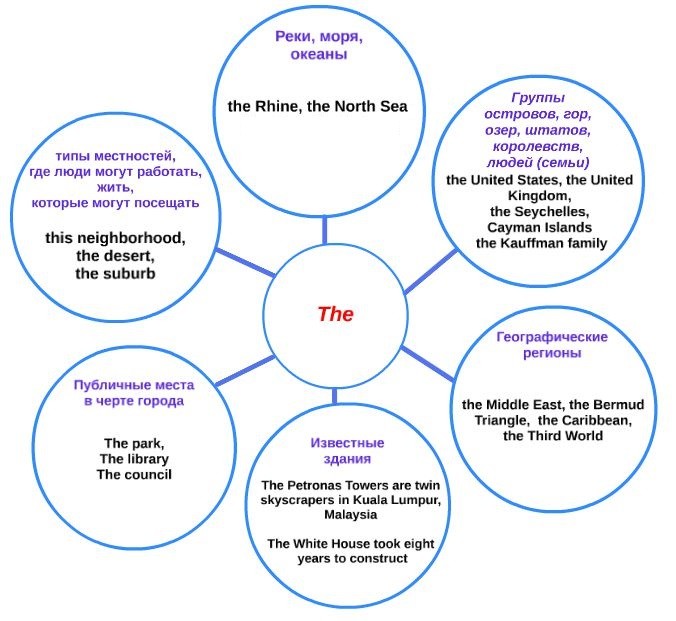
A definite article with geographical names and concepts
With those concepts that somehow relate to geography, the article the is used especially often.
1. Cardinal points: the East.
2. Names of individual countries: the Russian Federation.
3. Oceans, seas, rivers, waterfalls: the Indian Ocean.
4. Groups of islands, lakes, mountains: the Bahamas.
5. Deserts and plains: the Great Plains.

When using the article (or its absence) with geographical names, there are also many exceptions, so the simplest memorization is the most reliable option. And if in doubt, you should always look into the grammar guide and clarify the issue on a specific occasion.
Certain Occasions
There are also a number of words that can fulfill the function of defining a noun. These words are given in the table below.
previous |
|
past, past, last |
|
only |
|
following |
|
following |
|
upcoming |
|
right right |
|
central |
|
exactly the one |
|
not the wrong one |
|
the same |
|
upper, higher |
|
They always need to use the English article the. For example:
This is the very book I need! “This is exactly the book I need!”
The last time I saw him was Friday - The last time I saw him on Friday.
A definite article is also required before the words:

A definite article to enhance meaning
Situations are highlighted separately when the article the carries a stylistic function. In these cases, it can be used in front of proper names, which under normal conditions remain without the article. This is best seen in an example. Compare the two sentences: the first with the usual use of a proper name, and the second with a stylistic reinforcement of meaning.
This is Jack, always cheerful and generous! - This is Jack, always funny and generous!
This is the Jack I love most - cheerful and generous! - This is the same Jack that I love most - fun and generous!

As it is easy to see, there is something in common in all cases of the use of a certain article: usually it is put before words that carry a specific, concrete, narrow, unique meaning. Remember this when you doubt the choice of a service word, but the directory is not at hand.
Articles are the main identifiers of names nouns. Before using any noun, it is necessary to decide whether it is specific or indefinite, i.e. you need to imagine what kind of subject we are talking about: a specific or any.
In English, the article is almost always used before nouns:- Articles a and an are called uncertain article (the Indefinite Article)
- The bears the name certain article (the Definite Article)
We consider three cases: when the indefinite article is used before the noun, when the definite article is used, and when the article before the noun is not used.
Indefinite article
a - used before words starting with a consonant.
an - used before words starting with a vowel.
A noun with an indefinite article is the name of the subject in general, and not the name of a specific subject. For example, a student evokes an idea of \u200b\u200ba student in general, that is, a student of a higher educational institution, but not a specific person.
The value of the indefinite article can be expressed in Russian with such words as one, one of, some, some, some, everyone, any, everyone.
The indefinite article is used with countable nouns in the singular. It is not used in the plural, sometimes it is replaced by the indefinite pronouns some (several) any (any).
Definite article
The definite article has a single form: the. The individualizing article the descended from a demonstrative pronoun that - that one.
Missing article: zero article
Lack of indefinite article
The indefinite article is not used:
- before plural nouns
an article - articles
- nouns abstract
imagination - imagination - nouns mi tangible, uncountable (nouns that cannot be counted, for example, you cannot say: three waters).
water (water), salt (salt), tea (tea)
If there is a definition before a noun, then the article is placed before this definition:
a story
an interesting story
Coaster Rule
The use of the indefinite article
1. The indefinite article used before a noun when it only names an object, classifies it as a representative of a certain kind of objects, but does not specifically identify it.
- a table - any table (a table, not a chair)
a chair - chair
2. When mentioning an object or person for the first time
- That "s a pretty girl. - Beautiful girl
3. in a generic sense:
A noun with an indefinite article in this meaning means: any, any.
- A cow gives milk.
A cow (all) gives milk.
3. with professions:
- My Dad is a Doctor. “My dad is a doctor.”
She's an architect. - She is an architect.
4. with some expressions of quantity:
- a pair - pair
a little - a little
a few - a few
5. in exclamatory sentences: before a countable noun in the singular, standing after the word what.
- What a beautiful day! - What a wonderful day!
What a pity! - What a pity!
The use of a certain article
Definite article posed in the event that the subject or person in question is known to both the speaker and the listener (out of context, environment, or as previously mentioned in this speech).
- It is a chair - this is a chair
The chair is at the table - a chair stands near the table
Try substituting this or that word before a noun. If the meaning of the expressed does not change, then the noun must be given a definite article, and if it does, then the noun in the singular (if it is countable) is given the indefinite article, and the noun in the plural is not put at all.
1. Re-mentioned when it is clear from the previous text what this is about:
- The girl was beautiful. - (This) The girl was beautiful.
2. Clear from the situation when it is clear that / who means:
- The lesson is over. - The lesson is over.
3. Having an individualizing definition, that is, a definition that distinguishes this person or object from a number of similar ones.
- 3.1. Definition calling sign
:
This is the house that Jack built. - Here is the house that Jack built - 3.2. Definition expressed by the adjective in excellent formse
This is the shortest way to the river - This is the shortest way to the river. - 3.3. Definition expressed in ordinal
He missed the first lecture. - He missed the first lecture - 3.4. Definition proper noun
the Bristol road - the road to Bristol. - 3.5. Definitions expressed in words:
The next stop is ours. - Our next stop.
4. Before nouns are one of a kind:
- the sun - the sun
the moon - moon
the Earth - Earth
the floor - floor (one in the room)
the sea - the sea (the only one in the area)
5. Before adjectives and participles turned into nouns, with the plural:
- the strong - strong the old - old men, the young - the youth,
Lack of article (zero article)
1. If there is a pronoun before a nounor nouns in the possessive case.
My room is large - My room is large.
2. The noun is used without the article in the plural in those cases:
- 2.1. when in the singular in front of him would be an indefinite article:
I saw a letter on the table. - I saw a letter on the table.
I saw letters on the table. - I saw letters on the table.
3. Countless material nouns.
water water, milk milk, chalk chalk, sugar sugar, tea tea, snow snow, grass grass, wool wool, meat meat and others.
4. Innumerable abstract nouns (abstract concepts).
weather weather, music music, power strength, knowledge knowledge, art art, history history, mathematics mathematics, light light, love love, life life, time time
I like music - I like music.
But at the same time, some abstract nouns expressing a variety of quality, state can be used with the unapproved article.
He got a good education. He received a good education.
In English, plural nouns may be prefixed, the pronoun some (any), or the qualifier may be absent.
Rules for the use of the pronoun some
If a Russian noun can be meaningfully put one of the words: several, some, some, some, some, the corresponding noun in the English sentence is the pronoun some (any).
If not one of these words can be put in front of a Russian noun, then there is no qualifier before the corresponding noun in the English sentence.
I bought some apples yesterday - I bought apples yesterday (several, some apples)
Add to favorites
Indefinite article a / an in English (the indefinite article) has two forms:
a [ə] - used before consonants. That is, if a word begins with a consonant, it is used a:
a book, a table, a man, a girl a computer a tomato, a yacht [ jɒt], a unit [ ˈJuːnɪt]
an [ən] - used before vowels. That is, if a word begins with a vowel, it is used an:
an apple an engineer an idea an orange, an answer, an hour [ˈ aʊə (r)]
Please note that the choice of the form of the indefinite article is determined not by spelling, but by pronunciation.For example, the word hour starts with a vowel, so we use the article an (an hour)although the consonant letter comes first h. Or, for example, the word yacht (yacht) spelled y, but the consonant sound [j] is pronounced, so choose a (a yacht). The use of different forms of the same article helps to make speech harmonious, light, natural. Try to say a apple or an book, and you will feel how difficult and uncomfortable it is.
Remember:
Indefinite article a / an used only with in the singular:a pen (a pen), a story (story), a chair (chair), a child (child), a flower (flower)
If a noun is used in the plural, then the indefinite article is absent. The absence of the article before the noun is usually called the “zero article”.
pens (pens), stories (stories), chairs (chairs), children (children), flowers (flowers)
When using the indefinite article a / an
Below you will find a description of the main uses of the indefinite article. a / an in English.
№1
Indefinite article a / an used when we first mention an item or person. In this case, we assume that our interlocutor does not know what or who we are talking about.
Yesterday I bought a handbag. - Yesterday I bought a handbag.
Until that moment, I did not say that I was going to buy a bag. That is, I mention this for the first time (my interlocutor does not know anything about this bag), hence the indefinite article a / an.
If you continue to talk about this bag, then the noun handbag (bag) will already be used with a specific article the, since this time the interlocutor knows what kind of bag in question:
Yesterday I bought a handbag. The handbag is very beautiful. - Yesterday I bought a handbag. The handbag is very beautiful.
Although a personal pronoun is most often used instead of a noun, it sounds more natural and avoids repetition:
Yesterday I bought a handbag. It is very beautiful. - Yesterday I bought a handbag. She is very beautiful.
№2
Indefinite article a / an used when we are not talking about a given (certain) subject or person, but simply about any, about some, about one of the group of the same objects or people. In other words, when we talk about an object or person in general, not referring to a specific skirt, work, handle or a dog:
I want to buy a skirt. - I want to buy a skirt. (some skirt, which I don’t know yet; I just know that I want a skirt, not a dress)
He refused to look for a job. - He refused to look for work. (some work)
Give me a pen, please. - Give me a pen, please. (any, any)
It is a dog. - This is a dog. (some dog, any dog)
When we are not talking about a specific subject or person, but about any, then further, if we need to re-designate it, we do not use personal pronouns or a specific article the. And again, we use the indefinite article a / an or pronoun one.
She wants a car but he says they don’t need one. “She wants a car, but he says they don't need her.”
or
She wants a car but he says they don’t need a car. “She wants a car, but he says they don't need a car.”
She wants to have a car (not a motorcycle, not a bike, but some kind of car, therefore a car), but he says that they don’t need a car (they don’t need any car at all, and not some particular one). Since in the second part of the sentence we are again talking about any / indefinite machine, we again use a car.
№3
Indefinite article a / an we also use to describe or give any information about what we have already mentioned. In this case, the adjective is often used before the noun. Please note that although the article precedes the adjective, it refers to the noun:
It is a beautiful place. - This is a beautiful place. (describe what kind of place it is)
He is a clever boy. - He is a smart boy. (characterize what kind of boy he is)
Do you live in a big house? “Do you live in a big house?” (we ask in which house)
When we talk about a person’s profession or work, we also use the indefinite article a / an:
She is a teacher. - She is a teacher.
I am a doctor. - I am a doctor.
№4
Historically Indefinite Article a / an descended from the numeral one. Hence the opportunity in some cases to replace the article a / an numeral one. Such a replacement is possible when the article a / an essentially means "one." For example, this value of the indefinite article is observed in numerals a hundred, a thousand, a million (million) and in the word a dozen (dozen)when used alone or in front of a noun:
This toy costs a thousand roubles. \u003d This toy costs one thousand roubles. - This toy costs a thousand rubles (one thousand rubles).
Give me a dozen, please. \u003d Give me one dozen, please. “Give me a dozen, please (one dozen).”
It is with the origin of the numeral one and the value of unity of the indefinite article is associated, which is especially manifested in the expression of measures of time, distance, weight or quantity:
This chocolate bar costs a dollar. - This bar of chocolate costs a dollar. (\u003d one dollar, we can replace a dollar on one dollar)
I’ll call you in an hour. “I'll call you in an hour.” (\u003d after one hour, we can replace an hour on one hour)
Can i have a kilo of tomatoes, please? - Can I have a kilo of tomatoes, please? (\u003d one kilogram, we can replace a kilo on one kilo)
Please note that the numeral oneinstead of article a / an should be used only if you want to emphasize that we are talking about just one subject or person, that is, when you want to be very accurate:
I have got one sister. - I have one sister. (not two sisters, not three, but only one)
I have got a sister. - I have a sister. (in this case, I just report that I have a sister)
The value of the singularity of the indefinite article can be seen in some stable phrases that convey a single act:
have a look - take a look
have a snack - have a bite
have a try - try, try
have a rest - relax
have a good time - have a good time
give a chance - give a chance
give a hint - hint
give a lift - give a ride
make a mistake - make a mistake
play a trick - play a trick
№5
Indefinite article a / an also used when it is necessary to designate the quantity per unit of measure. For example, when we talk about the price of oranges per kilogram, the amount of wages per month, the number of classes per week, or the speed of the car per hour. The noun denoting this very one unit of measure will be used with an indefinite article.
The oranges were 80 roubles a kilo. - Oranges cost 80 rubles per kilogram.
She works 8 hours a day. - She works 8 hours a day.
I go to aerobics twice a week. - I go to aerobics twice a week.
№6
Indefinite article a / an can also be used with some uncountable abstract nouns (e.g. humor - humor, hatred - hate, anger - anger, magic - magic) when they have an adjective with them. Typically, this use of the indefinite article is characteristic of the book style and expresses the author’s desire to emphasize the individual, special character of a particular abstract concept.
Please note that in the case described above the use of the indefinite article is not mandatory. If you do not want to highlight in a certain way the special character of any emotion, character traits, etc., the article a / an can not be consumed.
On a note
To learn to use the indefinite article a / an more or less automatically, try to form a rule in your head: use the indefinite article with countable nouns in the singular, when there is no other reason for using a certain article the or some other qualifier (possessive or indefinite pronoun).
